US Expenditures for Public Schools
PublicSchools.RdPer capita expenditure on public schools and per capita income by state in 1979.
data("PublicSchools")Format
A data frame containing 51 observations of 2 variables.
- Expenditure
per capita expenditure on public schools,
- Income
per capita income.
Source
Table 14.1 in Greene (1993)
References
Cribari-Neto F. (2004). “Asymptotic Inference Under Heteroskedasticity of Unknown Form.” Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 45, 215-233.
Greene W.H. (1993). Econometric Analysis, 2nd edition. Macmillan Publishing Company, New York.
US Department of Commerce (1979). Statistical Abstract of the United States. US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC.
Examples
## Willam H. Greene, Econometric Analysis, 2nd Ed.
## Chapter 14
## load data set, p. 385, Table 14.1
data("PublicSchools", package = "sandwich")
## omit NA in Wisconsin and scale income
ps <- na.omit(PublicSchools)
ps$Income <- ps$Income * 0.0001
## fit quadratic regression, p. 385, Table 14.2
fmq <- lm(Expenditure ~ Income + I(Income^2), data = ps)
summary(fmq)
#>
#> Call:
#> lm(formula = Expenditure ~ Income + I(Income^2), data = ps)
#>
#> Residuals:
#> Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
#> -160.709 -36.896 -4.551 37.290 109.729
#>
#> Coefficients:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) 832.9 327.3 2.545 0.01428 *
#> Income -1834.2 829.0 -2.213 0.03182 *
#> I(Income^2) 1587.0 519.1 3.057 0.00368 **
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#>
#> Residual standard error: 56.68 on 47 degrees of freedom
#> Multiple R-squared: 0.6553, Adjusted R-squared: 0.6407
#> F-statistic: 44.68 on 2 and 47 DF, p-value: 1.345e-11
#>
## compare standard and HC0 standard errors
## p. 391, Table 14.3
coef(fmq)
#> (Intercept) Income I(Income^2)
#> 832.9144 -1834.2029 1587.0423
sqrt(diag(vcovHC(fmq, type = "const")))
#> (Intercept) Income I(Income^2)
#> 327.2925 828.9855 519.0768
sqrt(diag(vcovHC(fmq, type = "HC0")))
#> (Intercept) Income I(Income^2)
#> 460.8917 1243.0430 829.9927
if(require(lmtest)) {
## compare t ratio
coeftest(fmq, vcov = vcovHC(fmq, type = "HC0"))
## White test, p. 393, Example 14.5
wt <- lm(residuals(fmq)^2 ~ poly(Income, 4), data = ps)
wt.stat <- summary(wt)$r.squared * nrow(ps)
c(wt.stat, pchisq(wt.stat, df = 3, lower = FALSE))
## Bresch-Pagan test, p. 395, Example 14.7
bptest(fmq, studentize = FALSE)
bptest(fmq)
## Francisco Cribari-Neto, Asymptotic Inference, CSDA 45
## quasi z-tests, p. 229, Table 8
## with Alaska
coeftest(fmq, df = Inf)[3,4]
coeftest(fmq, df = Inf, vcov = vcovHC(fmq, type = "HC0"))[3,4]
coeftest(fmq, df = Inf, vcov = vcovHC(fmq, type = "HC3"))[3,4]
coeftest(fmq, df = Inf, vcov = vcovHC(fmq, type = "HC4"))[3,4]
## without Alaska (observation 2)
fmq1 <- lm(Expenditure ~ Income + I(Income^2), data = ps[-2,])
coeftest(fmq1, df = Inf)[3,4]
coeftest(fmq1, df = Inf, vcov = vcovHC(fmq1, type = "HC0"))[3,4]
coeftest(fmq1, df = Inf, vcov = vcovHC(fmq1, type = "HC3"))[3,4]
coeftest(fmq1, df = Inf, vcov = vcovHC(fmq1, type = "HC4"))[3,4]
}
#> [1] 0.8923303
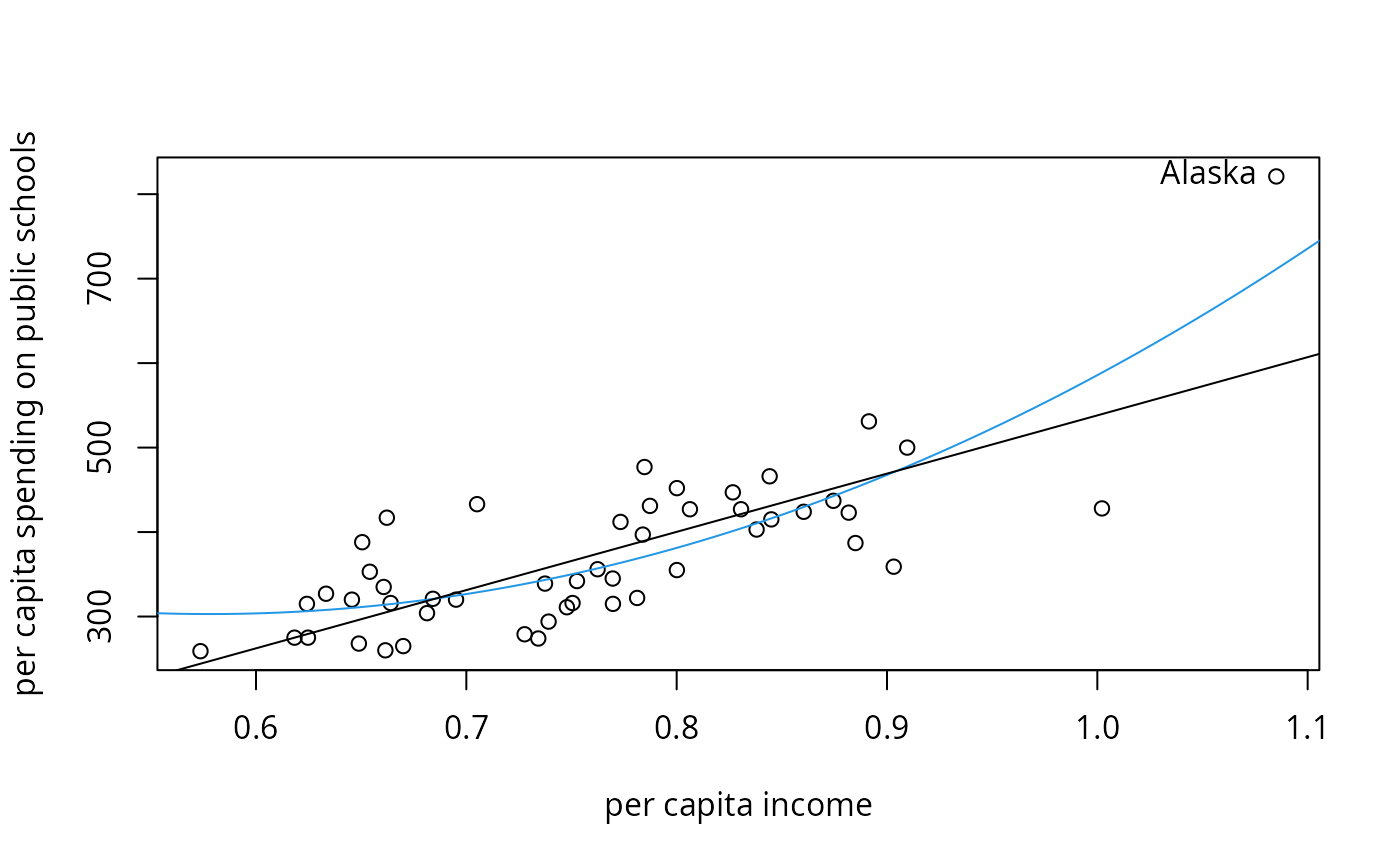
## visualization, p. 230, Figure 1
plot(Expenditure ~ Income, data = ps,
xlab = "per capita income",
ylab = "per capita spending on public schools")
inc <- seq(0.5, 1.2, by = 0.001)
lines(inc, predict(fmq, data.frame(Income = inc)), col = 4)
fml <- lm(Expenditure ~ Income, data = ps)
abline(fml)
text(ps[2,2], ps[2,1], rownames(ps)[2], pos = 2)